Embryo Transfer is the last step in IVF where the fertilized egg is inserted into a woman's uterus. This is one of the most important steps in the IVF process. During this step, an ultrasound is used to guide the physician in inserting the egg into the uterus.
Figure 1 shows the process of inserting a sperm cell into an egg, making it fertilized

Artificial Insemination is the process of a physician inserting sperm directly into a woman's cervix, fallopian tubes, and uterus. This aids men who have low sperm count and women who have problems with their reproductive organs in conceiving a child.
Artificial Insemination:Form of assisted reproduction
IVF works by fertilizing eggs inside a lab and having the fertilized eggs being inserted back into a uterus. This method of assisted reproduction is the most effective. However there are many cons to this method. The drawbacks include the operation being costly and intrusive.
IN vitro fertilization:Most popular form of assisted reproduction
Sex selection allows couples to determine the gender of the offspring before conception. The three motivations of sex selection are family balancing, genetic disorders, and preference of genders. This works by separating sperm based on the presence of X and Y chromosomes. These chromosomes determine the gender of the child. Females are XX and males are XY. The sperm is weighed and by using the difference of the weights, scientists are able to find out which sperm have the X or Y chromosome. These sperm are used for in vitro fertilization or artificial insemination, hence allowing couples to choose the gender of their child.
Sex Selection:Determines gender of offspring
Invention: Early 1900s
Cost: $300-$1000
Success Rate: Age<40:10% Age>40:5%
Invention: Robert Edwards, 1970s
Cost: $10,000-$30,000
Success Rate: Age<35:40% Age>42:4%

Cost: $3,000-$5,000 + Other Reproductive Treatments
Success Rate: 70%-99%

Surrogacy is a term used to define women who carries an embryo in their uterus. Their are two types of surrogacy: gestational and traditional. Gestational surrogacy refers to using IVF but instead of transferring the embryo to the mother, the embryo is transferred to a woman who is not genetically related to the embryo. Traditional surrogacy occurs when a woman is artificially inseminated and carries the baby for another couple. The baby is genetically related to the surrogate and is given to the couple for it to raise.
Surrogacy: form of assisted reproduction
Birth Control is defined as the devices and medications that are primarily used to prevent fertilization from occurring. Some forms of birth control are pills, condoms, spermicides, and Vasagel. Vasagel is a male alternative to condoms and is a solution that injected into the vas deferens which blocks sperm from being ejaculated. This method is still being developed and will be available to the general public soon. (See Timeline)
Birth control/contraceptives
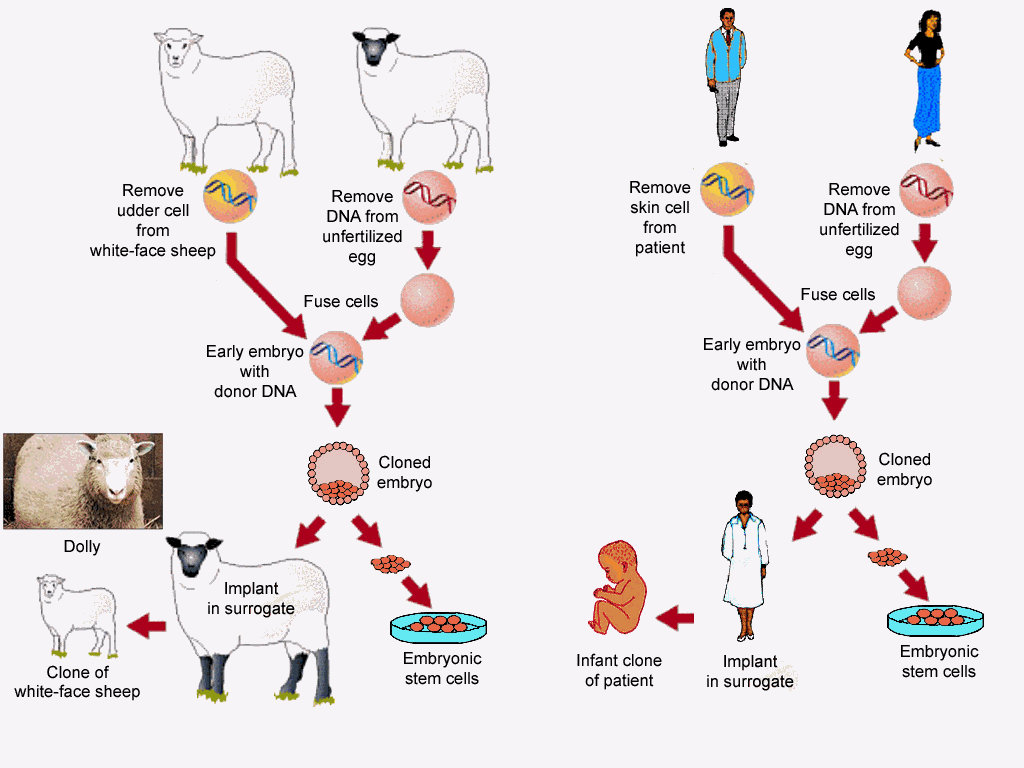
Cloning
Cloning a whole entire organism requires somatic cell nuclear transfer. To do this, an egg cell and a body cell is required. First, a somatic body cell is extracted from an animal and the nucleus of the cell is removed. Then the nucleus of the egg cell is extracted and replaced with the nucleus of the somatic body cell. The egg is then shocked with electricity which jumpstarts cell division. After that, the egg is inserted into a surrogate and develops as a normal egg would.
Applications for reproductive cloning include having a reliable group of animals for testing in science experiments, helping endangered species, and producing animals with desired genes.
Cryopreservation is the freezing of any body parts and reserving it for later use, specifically eggs, embryos, and sperm. The three scenarios in which cryopreservation is used are wanting to start a family in the future due to careers getting in the way, having extra embryos from an IVF cycle, and receiving medical treatments that may affect fertility. The method of freezing used for cryopreservation is called vitrification. Vitrification works by dipping cells into a cryoprotectant and and freezing it in liquid nitrogen. The cryoprotectant is used to protect the cells from freeze damage. Cryopreservation leads to the concern of what to do with extra eggs and embryos being frozen.
CryoPreservation: Assisted Reproduction technology (ART)
Success Rate: 2-4%

Invention: Hans Driesch, late 1800s
Cost: Animals: $20,000-$150,000
Cost: $15-$300
Success Rate: 70%-99%
Invention: 1970s
Cost: $100,000-$150,000
Success Rate: 45%-65%